Olive oil, often referred to as “liquid gold,” has long been celebrated for its culinary versatility and health benefits. Whether drizzled over a fresh salad, used to sauté vegetables, or as an essential ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine, olive oil has earned its place in kitchens around the world. But beyond its rich flavor and cultural significance, the quality of olive oil plays a crucial role in determining its effects on your health.
In this article, we will explore how the quality of olive oil impacts its nutritional value, health benefits, and potential risks. From the production process to the types of olive oil available in the market, understanding what goes into your bottle of olive oil can help you make better choices for your well-being.
Olive Oil: A Staple of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, known for its emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, has gained global recognition for promoting longevity and preventing chronic diseases. Olive oil, in particular, is a cornerstone of this diet. Rich in monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds, high-quality olive oil has been linked to improved heart health, reduced inflammation, and a lower risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and certain types of cancer.
But what exactly defines “high-quality” olive oil, and how does it compare to lower-quality alternatives? The answer lies in how the oil is made, the variety of olives used, and its overall composition. Let’s dive into the different types of olive oil and how their quality affects their health benefits.
The Different Types of Olive Oil
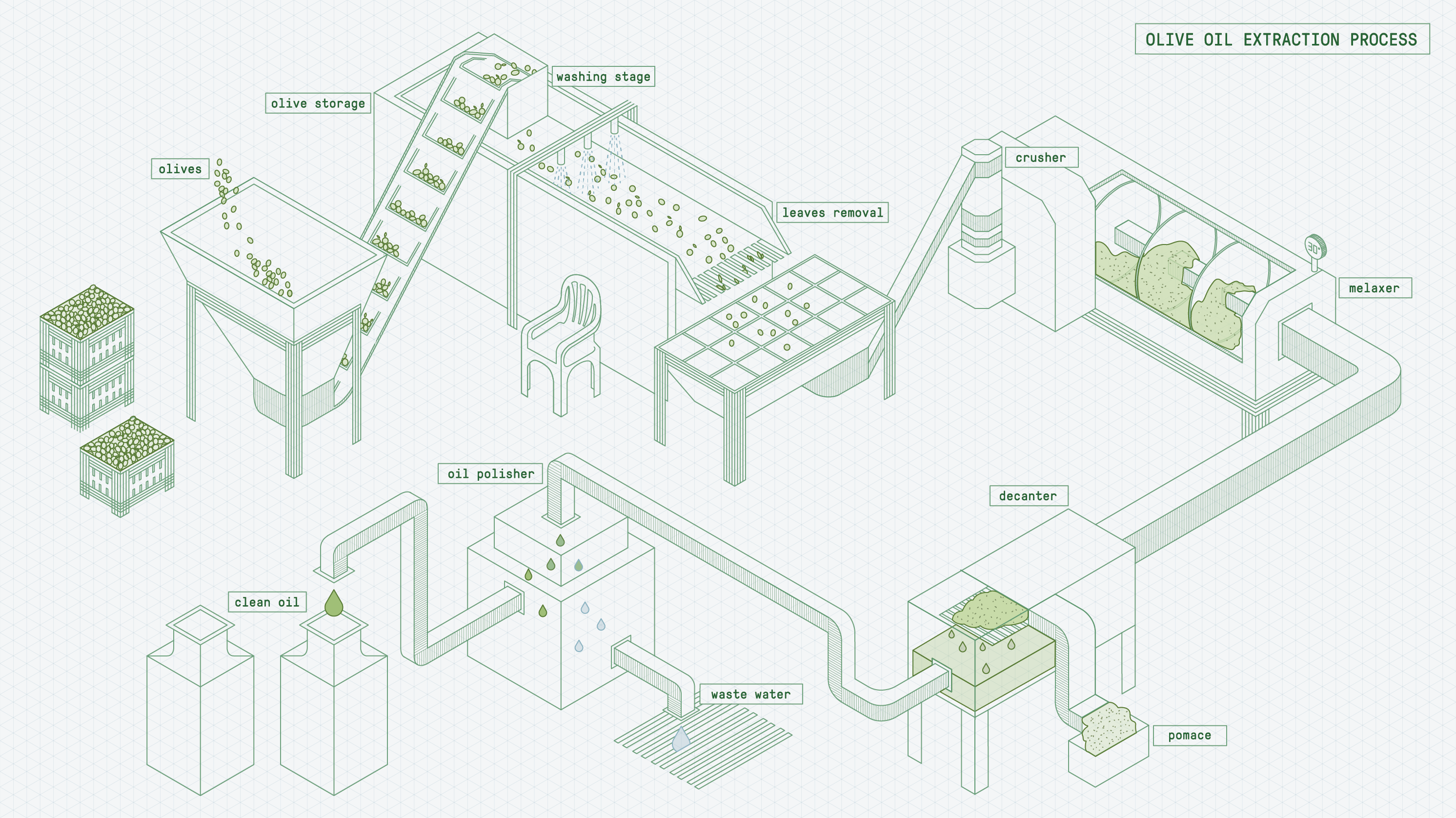
There are several grades of olive oil, ranging from extra virgin to refined varieties. The key difference lies in how the oil is processed and the level of refinement it undergoes. Let’s break down the most common types:
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)
Extra virgin olive oil is the highest quality olive oil available. It is made from the first cold pressing of olives, meaning no heat or chemicals are used in the extraction process. EVOO has the highest concentration of beneficial compounds, including monounsaturated fats, antioxidants (such as polyphenols), and vitamins like vitamin E. These components give EVOO its characteristic flavor, aroma, and health benefits.
The production of EVOO is strictly regulated, and for it to be classified as such, the oil must meet specific standards for acidity (less than 0.8%) and pass sensory evaluation tests for flavor and aroma. EVOO is also the least processed olive oil, which helps preserve its natural compounds and antioxidants.
Health Benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Heart Health: EVOO is rich in oleic acid, a monounsaturated fat that has been shown to lower bad cholesterol (LDL) levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Studies have consistently linked regular consumption of EVOO with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: The polyphenols in EVOO, such as oleocanthal, have potent anti-inflammatory effects, which can help reduce chronic inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is a contributing factor to many diseases, including arthritis, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Antioxidant Power: EVOO is packed with antioxidants, which help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and protect cells from oxidative stress. This can slow down the aging process and reduce the risk of developing various chronic diseases.

Virgin Olive Oil
Virgin olive oil is also made from the first cold pressing of olives but has a slightly higher acidity level than EVOO (up to 2%). While it is still of good quality, it has a less robust flavor and fewer antioxidants compared to extra virgin olive oil. Virgin olive oil may lack some of the delicate nuances found in EVOO, but it still retains many of its health-promoting properties.
Health Benefits of Virgin Olive Oil
- Virgin olive oil contains many of the same heart-healthy fats and antioxidants found in EVOO, though in slightly lower concentrations.
- It is still beneficial for inflammation and has moderate antioxidant properties, making it a good option for daily cooking and salad dressings.
Pure Olive Oil
Pure olive oil is a blend of refined olive oil and a small amount of virgin or extra virgin olive oil. The refining process removes most of the antioxidants and nutrients, leaving behind an oil that is more neutral in flavor and lower in beneficial compounds. While pure olive oil is still a healthier option than many other vegetable oils, it is a far cry from the nutritional power of EVOO.
Health Benefits of Pure Olive Oil
- Pure olive oil is lower in antioxidants and polyphenols compared to virgin or extra virgin olive oil, but it still provides healthy fats that can help improve cholesterol levels.
- It is suitable for high-heat cooking (like frying) because it has a higher smoke point than EVOO, but it lacks the rich flavor and health benefits that come with less refined oils.
Refined Olive Oil
Refined olive oil is made by refining virgin olive oil through processes such as bleaching and deodorizing, which strips away most of the oil’s natural nutrients, antioxidants, and flavor. While it is still technically olive oil, it is far less nutritious than its extra virgin counterpart.
Health Benefits of Refined Olive Oil
- Refined olive oil offers very few health benefits compared to EVOO. It still contains monounsaturated fats, but the refining process removes much of the oil’s beneficial compounds.
- This oil is better suited for high-heat cooking, such as frying, due to its higher smoke point.
The Role of Polyphenols and Antioxidants
The key to the health benefits of olive oil lies in its polyphenols and antioxidants. These compounds play a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, both of which are associated with the development of chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
Polyphenols
Polyphenols are plant-based compounds that act as antioxidants. In olive oil, they help protect the oil from oxidation, which can degrade the oil and reduce its health benefits. Polyphenols also have direct benefits for your body. They can reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation, and even enhance the body’s immune response.
One of the most studied polyphenols in olive oil is oleocanthal, which has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen. Regular consumption of olive oil with high polyphenol content can help lower the risk of chronic inflammation-related diseases.
Antioxidants
Olive oil is rich in vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative damage. The high antioxidant content of extra virgin olive oil is one of the reasons it is considered so beneficial for health. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, preventing damage to cells and tissues, which can lead to premature aging and a higher risk of disease.
Health Risks of Low-Quality Olive Oil
While high-quality olive oil can offer a wealth of health benefits, low-quality olive oil can do more harm than good. Low-quality oils, especially those that are refined or adulterated, may contain fewer nutrients and harmful substances, such as trans fats and excessive levels of oxidation by-products.
Rancidity
Over time, olive oil can become rancid, especially if it is exposed to light, heat, or air. Rancid olive oil loses much of its nutritional value and may even contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Always check the expiration date on your olive oil and store it in a cool, dark place to preserve its quality.
Adulteration
The olive oil industry has faced issues with adulteration, where cheaper oils such as soybean or sunflower oil are mixed with olive oil to cut costs. These oils often lack the beneficial compounds found in high-quality olive oil, making them nutritionally inferior. To avoid this, look for certified extra virgin olive oil that is traceable and has passed quality tests.
Choosing the Best Olive Oil for Your Health
When shopping for olive oil, it’s essential to choose one that will provide the most significant health benefits. Here are some tips for selecting high-quality olive oil:
- Look for Extra Virgin Olive Oil: As mentioned earlier, extra virgin olive oil is the most nutritious and health-promoting option. Make sure it is labeled as “extra virgin” and check for a low acidity level.
- Check the Harvest Date: Olive oil can degrade over time, so choose oil that is fresh. A good rule of thumb is to select oil that was harvested within the last year.
- Store Properly: Olive oil should be stored in a cool, dark place away from heat and light. Consider using dark glass bottles to protect the oil from sunlight.
- Buy from Trusted Sources: Look for olive oils from reputable producers who offer transparency about their production methods. Certifications such as PDO (Protected Designation of Origin) or organic labels can also provide assurance of quality.
Conclusion
The quality of olive oil plays a significant role in its health benefits. High-quality extra virgin olive oil is packed with beneficial compounds, including antioxidants and polyphenols, which can improve heart health, reduce inflammation, and protect against oxidative damage. On the other hand, lower-quality oils, such as refined or adulterated olive oils, offer fewer health benefits and may even contribute to health problems.
To get the most out of your olive oil, make sure to choose extra virgin olive oil, check the harvest date, and store it properly. With the right choice of olive oil, you can enjoy not only its rich flavor but also its wide-ranging health benefits.

